New Spectrophotometric Method for the Estimation of Isosorbide Mononitrate in Bulk and Tablet Formulation
Anjaly Pillai and P. N. Sanjay Pai
Department of Quality Assurance, Goa College of Pharmacy, Panaji - 403 001, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: pnsanjaypai@gmail.com
A validated simple, accurate and rapid spectrophotometric method was developed for the estimation of isosorbide mononitrate in bulk and tablet formulation. The method is based on the reduction of nitrate group of isosorbide mononitrate to nitrite ion by zinc/sodium chloride. Sulphanilamide undergoes diazotization with nitrite ion formed during reduction process in presence of hydrochloric acid. The diazonium salt is then coupled with N-(1-naphthyl) ethylene-diamine dihydrochloride (NED) to form a coloured product which is measured at 540 nm. The method was optimised for the amount of reagents required. Under the optimized experimental condition, Beer’s law is obeyed in the concentration range of 5-60 μg ml-1. The average percentage recovery of the drug for the proposed method was found to be in the range of 105.7-106.6% indicating no significant interference from tablet excipients.
KEYWORDS:Isosorbide mononitrate; N-(1-naphthyl) ethylene-diamine dihydrochloride; spectrophotometry; sulphanilamide
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Pillai A, Pai P, N. S. New Spectrophotometric Method for the Estimation of Isosorbide Mononitrate in Bulk and Tablet Formulation. Orient J Chem 2013;29(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Pillai A, Pai P, N. S. New Spectrophotometric Method for the Estimation of Isosorbide Mononitrate in Bulk and Tablet Formulation. Orient J Chem 2013;29(2). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=22254 |
Introduction
Isosorbide mononitrate (1,4,3,6-dianhydro-D-glucitol 5-nitrate)1 is a cardiovascular drug classified under organic nitrates. Isosorbide mononitrate is a drug used principally in the treatment of angina pectoris caused by coronary artery disease. It acts by dilating the blood vessels so as to reduce the blood pressure2 and increase the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart while reducing its workload3.
Isosorbide mononitrate is used for the prophylactic treatment of angina pectoris that is taken in order to prevent or at least reduce the occurrence of angina. Research on isosorbide mononitrate as a cervical ripener to reduce time at hospital for birth is supportive2.
From literature survey few analytical methods where found reported for the estimation of isosorbide mononitrate, that includes HPLC, HPTLC1, differential pulse polarography4 and liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry5. Based on the chemistry of isosorbide mononitrate that forms nitrite it was proposed to develop simple and economical methods for routine development of isosorbide mononitrate.
A simple, sensitive accurate rapid and economical validated visible spectrophotometric method for the determination of isosorbide mononitrate is now described.
The nitrate group of isosorbide mononitrate was reduced to nitrite ion with zinc/sodium chloride. The nitrite formed on reduction shows diazotisation reaction with sulphanilamide in presence of hydrochloric acid, which was then coupled with N-(1-naphthyl) ethylene-diamine dihydrochloride to produce an azo dye that has maximum absorbance at 540 nm (Fig 1). The proposed method was optimized.
Experimental
Apparatus
A Perkin Elmer lambda 25 UV-Visible spectrometer with matching quartz cells were used for the absorbance measurements.
Reagents and Standards
Reference standard sample of isosorbide mononitrate was kindly provided by Wallace Pharmaceuticals, Ponda, Goa, India. The commercial dosage form of isosorbide mononitrate Ismo (Abbott Healthcare Pvt Ltd, Baddi, India) was purchased from the local market.
All chemicals used were of analytical grade and distilled water was used in the preparation of all solutions. Standard solution of isosorbide mononitrate (1mg mL-1) was prepared in distilled water. Sulphanilamide (1% w/v) and N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (1% w/v) was also prepared in distilled water.
Zinc/sodium chloride mixture was prepared by mixing 0.5 g of zinc with 100 g of sodium chloride.
Procedure
Development of Standard Colour for Isosorbide Mononitrate
Volume of 10 ml of standard isosorbide mononitrate solution, 1mg ml-1 was transferred in to a beaker containing conc. Hydrochloric acid and 1ml of zinc/sodium chloride granular mixture and was heated in a water bath for 30 min with occasional stirring, then the solution was filtered through a whatmann filter no. 42 and transferred to 100 ml standard flask and diluted up to the mark.
Aliquots of standard solution containing 5-60 µg mL-1 of reduced nitrate were transferred into series of 10 ml standard flask and further mixed with 2 ml each of 1% w/v sulphanilamide solution and shaken for 5 min for completion of diazotization reaction. Further 2 ml each of N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (1% w/v) was added to form an azo dye and then the volume was made up to 10ml with water. The absorbance of the coloured azo dye was measured at 540 nm against reagent blank and the standard calibration plot was recorded (Fig 1).
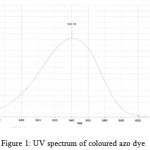 |
Figure 1: UV spectrum of coloured azo dye
|
Determination of Isosorbide Mononitrate in Marketed Tablet Dosage Formulation
Ten tablets were weighed and grounded. Powder equivalent to 25 mg of Isosorbide mononitrate was weighed accurately and dissolved in 10 ml distilled water. The resulting solution was filtered through whatmann no.42 paper. Then the filtrate was diluted to 25 ml with water. The procedure given under Development of standard colour was then followed for development of colour.
Optimization of Reagent Volumes and Conditions
The volume of reagent concentrations required for obtaining maximum absorbance for the solutions has been optimized.
Further, with optimized conditions, the proposed method has been validated for linearity, accuracy, precision, sensitivity, reproducibility and stability of colour. Recovery studies were carried out by mixing standard solutions of the drug at 3 different levels with previously analyzed tablet samples of isosorbide mononitrate. The results of the validation study and recovery study is presented in Table I and Table II, respectively.
Table 1: Validation Parameters:
| Parameters | Observations |
| Linearity | 5 – 60 mg mL-1 |
| Precision | 1.06% RSD |
| Sandell’s sensitivity | 3.6X10-3µg cm-2 |
| Equation of linearity graph | 0.0037X – 0.0104 |
| Slope: | 0.003 |
| Intercept: | 0.0104 |
| Stability of Colour | >24 hours |
Table 2: Recovery Study of Isosorbide mononitrate from Tablet samples:
|
Concentration of sample (mcg mL-1) |
Concentration of standard added (mcg/ml) |
Absorbance 540 nm* |
Concentration from graph |
% deviation |
|
7.5 |
0.0631 |
18.5 |
105.7 |
|
|
10 |
10 |
0.0726 |
21 |
105 |
|
12.5 |
0.0821 |
24 |
106.6 |
Results and Discussion
Zinc is one of the most frequently used reducing agent for the reduction of nitrate into nitrite ion, while sodium chloride is used to assist the reduction process6-8. Isosorbide mononitrate possesses a nitrate group which on treatment with Zinc/sodium chloride yields a nitrite ion. The nitrite ion thus obtained undergoes diazotization reaction with sulphanilamide in presence of HCl and then subsequently coupling with N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride to give a purplish-pink or violet coloured product that absorbs maximum at 540 nm. The reaction sequence is shown in Scheme.
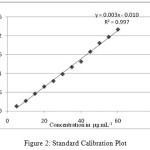 |
Figure 2: Standard Calibration Plot Click here to View figure |
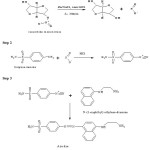 |
Scheme 1: Reaction sequence for the Formation of coloured product
|
A linear relationship was observed within isosorbide mononitrate concentration range 5-60 µg mL-1 as shown in Fig. 2. The precision was high as found from RSD of 1.06%. The sensitivity of method was found to be satisfactory as found from sandell’s sensitivity which was calculated from 3.6X10-3 µg cm-2. The colour was found to be stable for more than 24 hours and the accuracy of the method was determined where by standard sample of isosorbide mononitrate was added to previously analysed sample of isosorbide mononitrate at 3 different levels (75-125%). Recovery ranging from 105-106.6% was observed.
Conclusion
The proposed method is based on the reduction of nitrate group of isosorbide mononitrate into nitrite ion, diazotisation of sulphanilamide with liberated nitrite in acid medium and subsequently coupling with NED. The reagents provide a simple, sensitive and accurate method for the spectrophotometric determination of isosorbide mononitrate. The developed method does not involve any stringent reaction conditions and offers the advantages of colour stability for more than 24 hours.
References
- Yogeshwari S. Bhangle, Santosh V. Gandhi, Padmanabh B. Deshpande and Sachin E. Potawale. A validated HPTLC method for simultaneous estimation of metoprolol succinate and isosorbide mononitrate in combined dosage form. Int J Pharm Sci, 4(4); 2012: 217
- DrugBank: Isosorbide Mononitrate (DB01020), http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01020, (5 january 2013)
- Isosorbide Mononitrate (Oral Route) – MayoClinic.com – mayo clinic, http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/drug-information/DR602949, (11 January 2013)
- Pinzauti S, La Porta E, Gratteri P, Papeschi G and Giannellini V. Determination of isosorbide mononitrate in tablets by differential pulse polarography. Pharm Acta Helv. 64(4); 1989:125
- Hohyun Kim, Jae-yong Lee, Ki-Seob Song, Young-Hawan Seo, So-Young Park, Kyeong-Ho Kim, Hyun Dong Je, Sang Beom Han and Ji Hoon Jeong simultaneous separation and determination of isosorbide dinitrate and isosorbide 5-mononitrate in human plasma by LC-MS-MS. Chromatographia, 71(7-8); April 2010: 595-602
- Nafisur Rahman, Masoom Raza Siddiqui and Syed Najmul Hejaz Azmi. Quantitation of nicorandil in pharmaceutical formulations by spectrophotometry using N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride as coupling agent. Yakugaku Zasshi, 127(2); 2007: 367-374
- James C. Fanning. The chemical reduction of nitrate in aqueous solution. Coordination chemistry Reviews, 199 (2000): 159-179.
- Badiadka Narayana and Kenchaiah Sunil. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of nitrite and nitrate. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 4(2); 2009: 204.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









