Isolation and Identification of γ-sitosterol by GC-MS from Roots of Girardinia heterophylla
Nisha Tripathiathi1*, Sunita Kumar1, Rakesh Singh2, C. J. Singh3, Prashant Singh4 and V. K. Varshney5
1Department of Chemistry, M.K.P.P.G. College, Dehradun, India.
2Deprtment of Chemistry, D.B.S.P.G. College, Dehradun, India.
3Forest Conservation Division, Ministry of Environment and Forest, Delhi, India.
4Department of Chemistry, D.A.V.P.G. College, Dehradun, India.
5Chemistry Division, Forest Research Institute (FRI), Dehradun, India.
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/290245
The unknown compound of code number (GHRPTB) was isolated from roots of Girardinia heterophylla. After being collected and analyzed by GC-MS and compared with NIST standard chart library, it was declared to be γ-sitosterol, an epimer of β- sitosterol.
KEYWORDS:Girardinia heterophylla; GC-MS; γ-sitosterol; β-sitosterol
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Tripathiathi N, Kumar S, Singh R, Singh C. J, Singh P, Varshney V. K. Isolation and Identification of γ-sitosterol by GC-MS from Roots of Girardinia heterophylla. Orient J Chem 2013;29(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Tripathiathi N, Kumar S, Singh R, Singh C. J, Singh P, Varshney V. K. Isolation and Identification of γ-sitosterol by GC-MS from Roots of Girardinia heterophylla. Orient J Chem 2013;29(2). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=22217 |
Introduction
Girardinia heterophylla, commonly known as ‘DansKandali’, is abundantly found in the Himalayas. It can be seen growing extensively as an underutilized biomass in the forest areas situated in outskirts of the villages. The local people of Uttarakhand (India) used its roots as soap/shampoo and the whole plant is used as cattle fodder to improve milk production. It is also used as a bandage material for faster healing of wounds and setting of broken bones. β-sitosterol is the common sterol found in almost plants which hasΔ5 double bond and α- ethyl at C-24 [1]. In the present investigation the roots were collected, isolated and indentified by GC-MS.
Materials and methods
The plant samples were collected from the Middle Himalayas at an altitudinal range of 22,00m to 25,00m in Mussoorie hills. The plant samples (roots) were collected in the month of November 2010. A site of sample collection has been shown in the Figure-1 and it was confirmed from Systematic Botany Division, Forest Research Institute, Dehradun, Uttarakhand (India).
 |
Figure 1: Map Showing Sample Collection Site, Mussoorie hills (Uttarakhand) Click here to View figure |
Isolation and identification of unknown compound
The roots (600g) of Girardinia heterophylla were milled after air drying and were soxhlet extracted with the solvent petroleum ether (60-80oC) under vacuum yielded petroleum ether extract (2.57%) was column chromatographed over silica gel and elution of the column with varying amount of ethyl acetate in petroleum ether afforded one compounds.
Weight of petroleum ether extract = 15.42gm
Weight of silica gel used for adsorption of extract = 75gm
Weight of silica gel used for building of column = 322gm
Solvent used for packing column = Petroleum ether
Retention volume = 435
Volume of each fraction = 100 ml
The unknown compound of code number GHRPTB was eluted with petroleum ether: ethyl acetate (97:3) fraction number 133-283, volume 150x100ml on concentrating yielded white crystals (30mg, 0.01% and m.p.147-148oC). Solvent system for TLC was Petroleum ether: Ethyl acetate (93:7).It gave the Liebermann-Burchard test and was soluble in chloroform. The compound was analyzed by GC-MS. The mass spectrum of the compound was matched with that of γ-sitosterol provided in the NIST standard chart library, which led to the identification of γ-sitosterol.
2.3 GC-MS analysis
GC-MS condition for analyzing the unknown compound were TRAC-MS (Finnigancompany), OV-1071 column (30m x 0.25mm x 0.25μm) from vertical chromatography Co. Ltd. Mobile phase: He gas (99.99% purity), flow speed was 0.81/min, split ratio was 10:1. Sample temperature: 280oC. Column temperature: from 240oC and rose up to 265oC at the rising speed of 10oC/min. Remained at 265oC for 10 minutes. Ionization mode: EI+, Electron energy: 70eV. Interface temperature: 250oC. Ion source temperature: 200oC. Detection voltage: 350V, sample loading 0.5μl.
Results and discussion
Analysis of the unknown compound
The unknown compound was collected and analysed by GC-MS. The information of MS was given from the NIST standard chart library. The MS information is given in Figure-2. The unknown compound (Figure-3) probably was an isomer of β-sitosterol. In β-sitosterol the 24 ethyl substituent has α-chirality and in unknown compound the chemical structure is same as that of β-sitosterol only difference is that the 24 ethyl has β-chirality. Hence the given GC-MS information was given and shown that the unknown compound was probably to be an epimer of β-sitosterol, which was called γ-sitosterol.
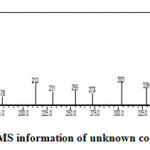 |
Figure 2: MS information of unknown compound. Click here to View figure |
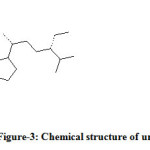 |
Figure 3: Chemical structure of unknown compound. |
γ-sitosterol is important plant sterols and has been reported first time in Girardinia heterophylla. γ-sitosterol reduces the hyperglycemia in STZ- induced diabetic rats due to increased insulin secretion and inhibition of glucogenesis. It can be used in Diabetes mellitus [2]. Docking studies of the ligand γ-sitosterol with four different target proteins showed that this is a good molecule which docks well with various targets related to Diabetes mellitus, thus γ-sitosterol can be considered for developing into a protein antidiabetic drug [3] It has been also reported that γ-sitosterol may affect the amount and activity of components of the extrinsic apoptic pathway in human lung and breast adenocarcinoma cells [4].
Present, investigation, provides an avenue for taking up future research and development activities for strengthening the existing pharmacological sciences besides, refining and utilizing traditional knowledge for the welfare of the society. Findings of the present study may be utilized to develop resource based local livelihood practices by screening of the economically viable and commercially important chemical compound from the all plants inhabiting predominantly in the hilly areas.
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge Uttarakhand Bamboo and Fiber Development Board (UBFDB) Dehradun for technical guidance
References
- Piironen, V., Lnsday, G. D. and Miettinen. (2000); Plant sterols: Biosynthesis, biological function and their importance to human nutrition, J. Sci. of Food and Agric., 80, 939.
- Balamurugan, R., Duraipandiyan, V. and Ignacimuthu, S. (2011); Antidiabetic activity of γ-sitosterol isolated from Lippianodiflora L. in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats, European J. of Pharmacol., 667, 410.
- Balamurugan, R., Stalin, A. and Ignacimuthu, S. (2012); Molecular docking of γ-sitosterol with some target related to diabetes, European J. of Med. Chem., 47, 39.
- Sundarraj, S., Thangam, R., Sreevani, V., Kaveri, K., Gunasekaran, P., Achiraman S. and Kannan, S. (2012);γ-sitosterol from Acacia nilotica L. induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through c-Myc suppression in MCF-7 and A549 cells, J. of Ethnopharmacol., 141, 803.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









