Green Synthesis and Charcterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Leafs Extracts of Rosa indica and its Antibacterial Activity Against Human Pathogen Bacteria
Amrita Raj1 , Reena lawerence2, Kapil Lawrence3, Neha Silas4, Mohd. Jaless5 and Rashmi Srivastava6
, Reena lawerence2, Kapil Lawrence3, Neha Silas4, Mohd. Jaless5 and Rashmi Srivastava6
1,2,4,5Department of Chemistry, Sam Higginbottom, University of Agriculture Technology and Science Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh 211003, India.
3Department of Molecular and Cellular Engineering, Sam Higginbottom, University of Agriculture Technology and Science, India.
6Department of Chemistry, Maharishi University, School of Science, lucknow, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: amrita21101992@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/340135
This work was carried out for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and investigation of its antibacterial activity. Rosa indica is of considerable interest and is well known compound because of its antioxidant, antidibetic , anti-inflammantry, antimicrobial activities. In the present study rapid and facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles at room temperature has been shown. On addition of plant extracts to Silver nitrate solution the change in color of the reaction mixture was obsereved which proved the formation of nanoparticles.Further , the green synthesised silver nanoparticles were characterized UV-Vis spectrophotometer, XRD analysis, FTIR, DLS, SEM with EDX .The average particles size of silver nanoparticles show between 1-100nm through DLS anaylsis. Antibacterial activity of the Silver nanoparticles was evaluated by testing against Gram – negative (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Gram – positive( Bacillussubtilis) bacteria.
KEYWORDS:Green Synthesis; Rosa Indica; Silver Nanoparticles; Antibacterial Activity
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Raj A, lawerence R, Lawrence K, Silas N, Jaless M, Srivastava R. Green Synthesis and Charcterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Leafs Extracts of Rosa indica and its Antibacterial Activity Against Human Pathogen Bacteria. Orient J Chem 2018;34(1). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Raj A, lawerence R, Lawrence K, Silas N, Jaless M, Srivastava R. Green Synthesis and Charcterization of Silver Nanoparticles from Leafs Extracts of Rosa indica and its Antibacterial Activity Against Human Pathogen Bacteria. Orient J Chem 2018;34(1). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=42528 |
Introduction
Nowdays, we are witnessing the development and advancement of a new interdisciplinary scientific field nanoscience.1As was shown by numerous example in physics, chemisty and biology, a transition from macrosizes to those of 1-100 nm gives size to qualitative change in physicochemical properties of individual compounds and system. The dependence of physicochemical properties on the partical size was magnetic properties, thermodynamics , electrochemistry, conductivity and electron transport.Nanochemistry or Nanotechnology related with the production and reactions of nanoparticles and their compounds.2-4It is concerned with the unique properties associated with assemblies of atom or molecules on a scale between that of the individual building blocks and the bulk material ( from 1 to 1000),5At this level, quantum effect can be significant , and also new ways of carrying out chemical reation become possible.6The science we methodologies from the synthetic chemistry and the material chemistry to obtain nanometerial with specific size, shapes, surface properties.Cross disciplinary nanoscience research involving physicts, chemists and engineers is concerned about the need of developing ecofriendly and sustainable methods for the synethesis of nanomaterials.7-9
There are many method for the synthesis of nanopartilces but one of the most conventional method is green synthesis because it is ecofrendily, non-toxic, very less expensive and very pure method. Nanoparticles having unique properties arising from their nanoscale dimensions.10-12 Nanoparticles has many important properties and various application in many areas such as drug, food, nutrition, electronics etc. 13The biological synthesis of nanoparticles which is very monodispersied particles with very specific sizes and shapes. The huge application in application in phamacutical company for successful remedical treatment as for disease. Green synthesis nanoparticles have great properties, which is synthesised by every part of plant such as, root, leaf, stem, flower, bark etc.14In Synthesis of nanoparticles dried from are used. In Every plant have terpenoids ,alkanoids, Flavanoid, total phenolic content, which is help to synthesied the nanoparticles. 15
The most researchers studied about nanoparticles . Today those nanoparticles are synthesised which are noble metals like silver, zincoxide, gold, lead etc. But among the nanoparticles, silver and zincoxidenanopartilces play a excellence role in the field of biological and drug industry. There are two type of approach for the synthesis of nanparticles –16
Top – down approaches
Bottom – up approaches
Thevery good effect show bottam – up approach as compared to top- down approaches. The bottom – up approaches show best results to produced the nanoparticles without any defects.17
Their many potential for human health.Biosynthesis of silver and zincoxie nanoparticles by plant, bacteria, fungi, and yeast. There are many routes for the synthesis of nanoparicles such as biological, chemical, physical, hydrothermal, electrochemical, irradiative, photochemical method.but green synthesis method has one of the best method for the synthesis of nanoparticles.18-19
Rosa indica is a traditional medicinal plants and its belonging family Rosaceae.20This plant have showing greatest advantages for stomach problem, and are being investigation for controlling cancer growth, constripation, inflammation, leucorrhea, heart and eye disease. Buds and Petal of Rosa indica used for removal of gal bladder and kidney and flower are used against asthma. It is commonly cultivated for fiber and most edible purposes and many used in medicinal purposes. The plant have more medicine value show like antioxidant, blood pressure, antidipression, anticancer, diuretic, antifungal, anti-immammatory anti-carcinogenic activity.
Materials
Plant Collection
The fresh leaves of Rosa indica were collected from Department of Horticulture , SHUATS Allahabad (State University), India.
Chemicals
Silver nitrate was analytical grade. Ultra-purified water used throughout the research work to prepare solution from a Merkmillipore-Milli-Q water purification System. All glassware have been washed with sterile double distilled water and dried in an oven before use.
Methods
Preparation of Plant Extract21
Rosa indicaleaves were washed thoroughly under running deionised water and then rinsed thoroughly with ultra-purified water and dried at room temperature. The leaves are grinded to make a fine powder and used for experimental studies. The solution of leaf broth was prepared by taking 15 g leaves powder in a 150 ml ulta-purified water (deionized water) and then boiled 30 min at the temperature 600C. Then the leafs broth was cooled at room temperature then the leaf broth were filtrered using whatman filter paper before centrifuged at 3000rpm for 10 min for remove heavy metal and then leaf broth kept in refrigerators at 40Cfor further experimental use.
Phytochemical Analysis 22-23
Phytochemical analysis of leafs extracts of Rosa indicaananlysis by the spectra of UV-Vis spectrophotometer and FTIR.
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles21
5ml of leaf broth was added drop by drop to 45 ml of 1mM aqueous silver nitrate solution using magnetic stirrer at room temperature, the solution become brown in color. Then the solution was centrifuged 5000 rpm for 15 min. Then it show formation of silver nanoparticles.
Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
UV-Vis Spectrophtometer
UV-Vis spectroscopic studies were carried out on a Shimadzu UV-3600 Plus spectrophotometer at Mnnit Allahabad.
Dynamic Light Scatterring
The average Particle size of the synthesized silver nanoparticles was evaluated with the help of a Nano Microtrac total solution in particles at Mnnit Allahabad.
X-Ray Diffraction
Silver nanoparticles was examined by X-Ray diffraction analysis using Rigaku Smart Lab X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation monochromatic filter in the range of 10-900at Mnnit Allahabad.
Fourier transform- infra red
FTIR spectra of silver nanoparticles was recorded by Perkin Elmer Spectrum Version 10.4.00.at Mnit Jaipur.
Scanning Electron Microscopy with EDX
SEM study was carried out to investigation the shape, size, and the surface area of the silver nanoparticles by Zeiss at Iit Kanpur.
Anti-Bacterial Assay24
Anti-bacterial activities were studied against Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 121) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa(MTCC 1688) strain. The antibacterial activity of Green synthesizedof Silver nanoparticles was testedagainst variouspositiove and negative bacteria by the agar well diffusion method. To examine the antibacterial activity of Green synthesied Ag NPs Muller- Hinton agar plates were sterilized and allowed to solidify. After solidification, 10μl of each bacterial suspension was inoculated on the petriplates by a sterile glass rod.Then ,using sterile borer pounched four well into agar plates. Then we take three concentration, 25µl,50µl,75µl of silver nanoparticles was poured into well by the using of micropittete. Then we take a control (Amoxicillin) and the concentration of control is 25µl, which is poured in one well of the agar plates. After that incubated for 24 hrs and at 370C,The were observed around the discs. Antibacterial activity was investigation by measuring the diameter of the zones of inhibition.
Statistical Analysis
Two way of analysis variance (ANOVA ) using in the result of antibacterial activity.
Result and Discussion
The first confirmation of Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by observation, During the visual observation, when addition of leaves extract of Rosa indicato 1mM solution of silver nitrate then the color of the solution changed from pale yellow to brown. This color change indicate the formation of silver nanoparticles .27 In this reation show the reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles . The solution of color arises due to the excitation of surface plasma vibration in silver nanoparticles (Fig. 1.).
 |
Figure 1: Color Change indicating show formation of silver nanoparticles A) Rosa indica leaves extracts B) 1mMSolution of silver nitrate C) and D) show change the color from pale yellow to brown. Click here to View figure |
Phytochemical ananlysis of leafs extracts-
The phytochemical ananlysis of leaves extract was examined spectroscopically. Phytochemical analysis of leafs broths was confirm by the instruments of UV-Vis Spectroscopy and FTIR. It is given confirmation that total phenolic group, antioxidant content, flavonoids, amines etc. formed in the plant extracts, these compounds confirm by IR band Which is used to as capping agent for the reduction of silver ion to silver nanoparticels. showen in fig 2 (A) and 3(B). The UV-Vis spectroscopy confirm the presence of polyphenol in the leafs extracts. The absorbance of leafs extracts presented peak at 270nm as characteristic of polyphenol molecules.This result also in according of the reported literature.22 In FTIR Showing different functional groups in leaves extracts, that confirm the polyphenol groups present in plant extrats. Also this result are according of reported literatue.23
UV-Vis Spectrophotometer-
After observation, then the Green synthesised of silver nanoparticles was first characterized from UV-Vis spectrophotometer. At the different time interval, the complete the reaction of green synthesied of silver nanoparticles the maximum absorbance peak are observe at 425nm. In the green synthesied silver nanoparticles showing strong surface plasma resonace band at 420nm using Rosa indica leaves extrats.25 UV-Vis absorbance spectrophotometer is an most important chacterization for the showing the stability and formation of silver nanoparticles. In fig B showing complete conversion of silver ion to silver nanoparticles.
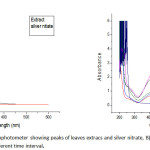 |
Figure 2: A)UV-vis spectrophotometer showing peaks of leaves extracs and silver nitrate, B) Confirmation of silver nanoparticles at different time interval. Click here to View figure |
Fourier transform- infra red
FTIR is the one the most important characterization technique for the detecting the functional group in plant extract and silver nanoparticles,26-30 which is indicating to confirmation of silver nanoparticles. For, the reduction of silver nanoparticles the functional group of leaves extract is responsible for the reduction of silver ions.
The peak intensity of the spectrum showing different region of functional group in leaves extract and silver nanoparticles are analysed and showing in figure 3.
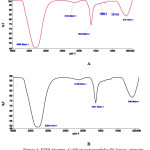 |
Figure 3: FTIR Spectra A) Silver nanoparticles B) leaves extracts Click here to View figure |
In FTIR spectra of silver nanoparticles and leaves extracts having more similarties with some difference between of position of peak.31-32 The most intense and broad peak was come in spectra at 3304 cm-1 corresponds to OH stretching vibrations of phenol and –COOH gorup present in leaves extracts. The peak located at 1635cm-1 it was showing and indicating C=O sterching and amide binding. At 2124cm-1 peak obsevedby the alkanes present due to stretching . The nitro N-O bending is assigned the peak at 1365cm-1 and at 1214 cm-1 peak showing to C-O-C streching aromatic ring. At 578cm-1 peak inicating to allkyl halides band For C-Cl. In FTIR spectra showing various gourp like carboxyl, carbonyl, amide, alkyl halide, phenol group of rosaindica leaves extracts are used for the Green synrhesis of silver nanoparticles . All goup are use as capping and stabilization agent in redytion of silver ion to silver nanoparticles.
X- Ray Diffraction (XRD)
The X-Ray diffraction characterization of sample was carried out to confirmation of Green synthesied silver nanoparticles.
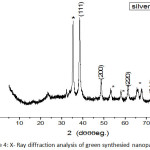 |
Figure 4: X- Ray diffraction analysis of green synthesied nanoparticles. Click here to View figure |
The five stong Bragg reflections formed at 2 theta value of 38.21o, 44.11o, 64.190, 77.56o,81.670 corresponding to (111), (200), (220), (311),(222). Silver nanoparticles indicating strong, narrowand crystalline nature.33-34 The size of silver nanoparticles was formed by Debye- Scherrer formula given by the equation
D=Kλ/ (β cos θ)
Where-
D- the crystal size
λ- the wavelength of the X-ray radition (λ= 0.15406nm) for CuKa,
K- usually taken as 0.89
Β- the line width at half- maximum height
In XRD analyisis showing structural peaks and approximately size of crystalline of nanoparticles around 45-85nm .the green synthesied of silver nanoparticles show nanocrystalline in nature.35 In XRD spectra show some extra peak, which is showed by stars, this peaks observed that the crystallization of bioorganic phase formed on the surface of Ag NPs. similar result was reported in silver nanoparticles using edible mushroom extract.38
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
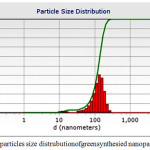 |
Figure 5: Showing particles size distrubution of green synthesied nanoparticles Click here to View figure |
In Dynamic light scattering used suspension of silver nanoparticles green synthesis from leaf exract from Rosa indica. The particle size distrubution though the DLS indicate the size of green synthesied nanoparticles between around10 to 127nm. In this Figure V the very small amount of green syntheised silver nanoparticles are agglomerated showing in fig.5.
Scanning electron microsopy with EDX
The solution of green synthesied of silver nanoparticles was formed by centrifuged at15000 rpm at 20 min, then the suspension and pellet are seperated the pellets again redispersed in ultrafine deionised water. The highly pure pellet was freeze then dried, then used for analysis. The surface morphology of silver nanoparticles was ananlysis using scanning electron microscopy with EDX. This figure show the confirmation of silver nanoparticles, which is synthesied by leafs extracts. The green synthesied silver nanoparticles were small amount agglomerated. The green synthesied of silver nanoparticles are spherical in shape.36 Silver nanoparticles was futher confirmation by EDX. In EDX figure showing strong peak which is indicating confirmation of Ag NPs.
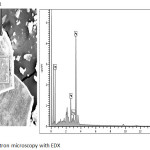 |
Figure 6: Scanning electron microscopy with EDX Click here to View figure |
Antimicrobial Activity
Antimicrobial acitivity was done by well diffusion method. The antimicrobial activity of Green synthesied AgNPs was accomplished against gram positive and gram negaitive bacteria. The green synthesied Silver nanoparticles having excellent antimicrobial activity against gram positive and gram negaitive bacteria. In this paper, the gram positive bacteria indicating the higestzone of inhibition and most effective as compared to gram negaitive bacteria. The higest zone of inhibition was observed for 15mm in B.subtilis and 14.5 in P.aeruginosa at the higest concentration 7.5 µg/µl. According to figure 25 µl concentration of amoxicillin showed mamxium radius of zone of inhibition of 21 against B.subtilis and 22.5 against P.aeruginosa. Silver nanoparticles have show most efficiency to inhibit the bacteria growth by the formation of reactive oxygen species and accumulation of nanoparticles. Silver nanoparticles act as bactericidal and bacteriostatic agents.37In this result, using the Statistical analysis by the annova software.
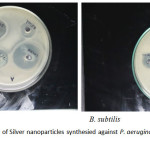 |
Figure 7: Antibacterial activity of Silver nanoparticles synthesied against P. aeruginosa and B. subtilis Click here to View figure |
Table 1: Zone of inhibition (mm) obtained from well diffusion methods
| Concentrationsµg/µl | Zone of inhibition (mm) | |
| P.aeruginosa | B.subtilis | |
| 25 | 7.9 | 8 |
| 5 | 13.9 | 14.5 |
| 75 | 14.9 | 15 |
Disc’s diameter- 5 mm
|
ANOVA : |
||||||||
|
Source |
d. f. |
S.S. |
M.S.S. |
F. Cal. |
F. Tab. 5% |
Result |
S. Ed. (±) |
C.D. at 5% |
|
Due to zone inhibition |
1 |
0.107 |
0.107 |
2.56 |
18.51 |
NS |
0.167 |
0.344 |
|
Due to Concentration |
2 |
59.083 |
29.542 |
709 |
19.00 |
S |
0.204 |
0.421 |
|
Error |
2 |
0.083 |
0.042 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
TOTAL |
5 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Conclusion
In this paper we study the Green synthesied of silver nanoparticles from leaves of Rosa indica. In this rection leafs extracts used as capping agent for the stability of nanoparticles. Silver nanoparicles having sheperical shape and size of 1-100 nm .its show excellent antibacterial activity against gram positive and gram neagaitive bacteria. Also, we confirmation of green synthesised silver nanoparticles by UV-Vis, XRD, DLS, FTIR, SEM, EDX. This is eco-frendly , non-toxic, very conventional method.
Acknowledgements
This authors wish to thanks MNNIT and SHUATS Allahabad for financial support and having given feasibilities to carry out the research work.
Reference
- Aragao, A.P.D.; Oliveira,T.M.D.; Quelemes,P.V.;Perfeito,M.L.G., Araujo.M.C.; Santiago,J.N.A.S.;Cardoso,V.S.;Quaresma,P.;Leite,J.R.D.S.D.A.;Silva,D.A.D.;Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the seaweed Gracilariabirdiae and their antibacterial activity,.Arabian Journal of Chemistry, (2016),1878-5352
- Rajeshkumar,S.; Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fresh bark of Pongamiapinnataandcharacterization of its antibacterial activity against gram positive and gram negative pathogens, ScienceDirectResource-Efficient Technologies,(2016) , 2 ,30–35
CrossRef - Nalwade . A.R., Sankala . K.D., Jagdale . K. B.;Poisonous weed leaf extract mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial activity,Research in Pharmacy,(2013),3(4), 09-15
- M. Umadevi, M.R. Bindhu, V. SatheA Novel Synthesis of Malic Acid Capped Silver Nanoparticles using Solanumlycopersicums Fruit Extract SciVerse Science Direct J. Mater. Sci. Technol., (2013),29(4), 317-322
CrossRef - Kim,J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu,K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park,S.J.;Lee,H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park,Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang,C.Y.;Kim,K.Y.; Yoon-Sik Lee,S.Y. ; Jeong, D.H., Cho, H.M.; Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles,Nanomedicine, Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine,(2007),3 ,95– 101
CrossRef - Abdel-Aziz.S.M.; Shaheen.M.S.; El-Nekeety.A.A.; Abdel-Wahhab.M.A.;Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using Chenopodiummurale leaf extract , Elsevier King Saud University, (2013),18,1319-6103
- Vignesh. V., Anbarasi. K,F., Karthikeyenia.S., Sathiyanarayanan. G., Subramanian.P., Thirumurugana.R.; A superficial phyto-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their assessment on hematological and biochemical parameters in Labeorohita (Hamilton, 1822) Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects.(2013), 439, 184– 192
CrossRef - Kumar,C,G.; Poornachandra.Y.;Biodirected synthesis of Miconazole-conjugated bacterial silvernanoparticles and their application as antifungal agents and drugdelivery vehicles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,(2015),125,110–119
CrossRef - Perni,S., Hakala.V., Prokopovich.P., Biogenic synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles capped withl-cysteine.Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, (2014),460, 219–224
CrossRef - Gavade. N.L., Kadam.A.N.,Suwarnkar.M.B., Ghodake.V.P., Garadkar.K.M.;Biogenic synthesis of multi-applicative silver nanoparticles by using ZiziphusJujuba leaf extract. SpectrochimicaActa Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,(2015). 136 ,953–960
CrossRef - Dubey, S.P., Lahtinen. M., Särkka.H., Sillanpaa.M., Bioprospective of Sorbusaucuparia leaf extract in development of silver and gold nanocolloidsColloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, (2010), 80 ,26–33
CrossRef - Singh.A.K., Talat.M., Singh.D.P., Srivastava.O.N.; Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles by naturalprecursor clove and their functionalization with amine group J Nanopart Res, (2010) 12,1667–1675
CrossRef - Vijayakumar.M., Priya.K., Nancy.F.T., Noorlidah.A.,, Ahmed.A.B.A.,Biosynthesis, characterisation and anti-bacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Artemisia nilagirica.Industrial Crops and Products, (2013) ,41 , 235– 240
CrossRef - V.K. Vidhu, D. PhilipCatalytic degradation of organic dyes using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles Micron, (2014) 56, 54–62
CrossRef - Barwal.I., Ranjan.P., Kateriya.S., Yadav.S.C.; Cellular oxido-reductive proteins of Chlamydomonasreinhardtii control the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles Journal of Nanobiotechnology, (2011)9, 56
CrossRef - Boopathi.S.,Gopinath.S., Boopathi.T., Balamurugan.T.,Rajeshkumar.R., Sundararaman.M., Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Silver and Silver Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized by Cell-Free Extract of a Mangrove- Associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa M6 Using Two Different Thermal Treatments Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. (2012), 51, 5976−5985
CrossRef - Zhang.Y., Gao.G., Qian.Q., Cui.D.; Chloroplasts-mediated biosynthesis of nanoscale Au-Ag alloy for 2-butanone assay based on electrochemical sensor Nanoscale Research Letters, (2012),7, 475
CrossRef - Sathishkumar.M.,Sneha.K., Won.S.W., , C.-W. Cho, S. Kim, Y.-S. Yun.;Cinnamon zeylanicumbark extract and powder mediated green synthesis of nano-crystalline silver particles and its bactericidal activity. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, (2009)73,332–338
CrossRef - Vanaja.M., Annadurai.G.,Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity ApplNanosci(2009),3, 217–223
- Mishra R.P.;ArshadM.;and Sami, A.;Antibacterial Properties of Rosa indica(L.) Stem, Leaves and Flowers, JPBMS, 2011, 12 (15)
- Balen. K., Qing.W.,wang.Y., Liu. X., Palvannan. T., Wang. Y., Ma. F., and Zhang .Y.,Antidiabetic activity of silver nanoparticles from green synthesis using lonicera Japonica leaf extract. RSC Advance(2016), 6, 40162-40168.
CrossRef - Leon,E.R.;Palomares,R,I.;Navarro,R.E.;Urbina,R.H.;Tonori,Judith.;Palomares,I.C.;Moldonado,A.;synthesis of silver nanoparticles using reducing agents obtained from natural sources Rumexhymensoplusextacts, Nanoscale Research letters, 2013,8, 318
CrossRef - Ahmed,S.;Ikram,S.; Silver nanoprticles : one pot green synthesis using TerminaliaarjunaExtact for Biological Application, J Nanomedicine Nanotechnology2015 ,6, 4
- A, R. Allafchian, S.Z. Mirahmadi, S.A.H. jalali, S.S hashemi, M.R.Vahabi (2016).Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using phlomis leaf extract and investigation of their antibacterial activity.Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry, (2016)..6, 129-135
- Song.J.,Wu.F., Wan.Y., Ma.y.;Colorimetric detection of melamine in pretreated milk using silver nanoparticles functionalized with sulfanilic acid. Food Control(2015) 50: 356-361
CrossRef - Hei.H., Hong H., Wang.R., Liu.L., Zhang.G., Controlled Synthesis and Characterization of Noble Metal Nanoparticles. Soft Nanoscience Letters,(2012) ,2: 34-40
CrossRef - S. Lokina., A. Stephen ., V. Kaviyarasan., C. Arulvasu ., V. Narayanan.; Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activities of green synthesized silver Nanoparticles European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, (2014)76 :256-263
CrossRef - Shankar.S., Chorachoo.J., Jaiswal. L., Voravuthikunchai. S.P., Effect of reducing agent concentrations and temperature on characteristics and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles. Materials Letters. (2014),137:160–163
CrossRef - Edison.T.N.J.I.,Sethuraman.M.G.,Electrocatalytic Reduction of Benzyl Chloride by Green SynthesizedSilver Nanoparticles Using Pod Extract of Acacia niloticaACS Sustainable Chem. Eng,(2013). 1:1326−1332
- Singh.A.K.,Tripathi.Y.B., Pandey.N.,Singh.D.P., Tripathi.D., Srivastava.O.N., Enhanced antilipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced changes in macrophage functions by Rubiacordifolia (RC) embedded with Aunanoparticles. Free Radical Biology and Medicine , (2013).65:217–223
- Mudasir A. D., Ingle.A.,Rai.M., Enhanced antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cryphonectria sp. evaluated singly and in combination with antibiotics. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine, (2013) 9:105–110
CrossRef - Pant.G., Nayak.G., Prasuna.R.G., Enhancement of antidandruff activity of shampooby biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from SolanumtrilobatumplantleafApplNanosci, (2013), 3:431–439
- Gunasekar.V.,Divya. B. Brinda. K.,Vijaykrishnan.J.,Ponnusami.V.,Rajan.K.S.,Enzyme mediated synthesis of Ag–TiO2 photocatalyst for visible light degradation of reactive dye from aqueous solution. J Sol-Gel SciTechnol, (2013),68:60–66
CrossRef - Mishra.A., Kaushik.N.K., Sardar.M., Sahal.D., Evaluation of antiplasmodial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, (2013)111: 713– 718
CrossRef - Zahir.A.A.,Rahuman.A..A.; Evaluation of different extracts and synthesised silver nanoparticles from leaves of Euphorbia prostrata against Haemaphysalisbispinosa and Hippobosca maculate Veterinary Parasitology, (2012)187:511– 520
CrossRef - Dhanasekaran.D.,Thangaraj.R.; Evaluation of larvicidal activity of biogenic nanoparticles against filariasis causing Culexmosquito vector Asian Pac J Trop Dis(2013),3(3): 174-179.
- Santhoshkumar.T., Rahuman. A. A., Bagavan.A., Marimuthu. S.,Evaluation of stem aqueous extract and synthesized silver nanoparticles using Cissusquadrangularis against Hippoboscamaculata and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Experimental Parasitology(2012) , 132 : 156–165
CrossRef - Philip. D.; Biosynthesis of Au, ag and Au-Ag nanoparticles using edible mushroom extract. Spectrochimica Acts Part A : Molecular and Biomolecular spectroscopy. (2009), 73, 374-381

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









