Synthesis and Characterization of Various Alkyl, Aryl and Hetero Aryl Substituted Hydrazines and Study of their Biological Activity
Poonam Goklani
Department of Chemistry, Govt. Dungar College, Bikaner, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: anil362@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/330262
Due to the presence of N-N linkage hydrazines are well-known for their diverse biological activity.N-N linkage has been used as a key structural motif in various bioactive agents. A series of aryl, alkyl and hetero aryl substituted hydrazine derivatives has been synthesized, for this diazotization of alkyl, aryl amines has been done, followed by reduction with stannous chloride or sodium sulfite. All synthesized compounds were characterized by elemental analysis, IR, 1H-NMR, Mass spectra and their biological activity has been studied.
KEYWORDS:Hydrazine derivatives; N-N linkage; Biological activity; Diazotization
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Goklani P. Synthesis and Characterization of Various Alkyl, Aryl and Hetero Aryl Substituted Hydrazines and Study of their Biological Activity. Orient J Chem 2017;33(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Goklani P. Synthesis and Characterization of Various Alkyl, Aryl and Hetero Aryl Substituted Hydrazines and Study of their Biological Activity. Orient J Chem 2017;33(2). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=31346 |
Introduction
Among the nitrogen-nitrogen bond containing chemical the hydrazines are well-known for their diverse biological activity and as therapeutic agents in medicines. Many hydrazine derivatives are known to exhibit significant biological activity and several compounds with hydrazine moiety were shown to be effective for treatment of tuberculosis, Parkinson’s disease and hypertension1.Hydrazinesshowsneuroprotective, antitumor antidepressant and antimicrobial properties2,3,4,5.
The hydrazine moiety has been used for modification of peptides6.Azapeptides hydrazine based peptidomimetics, were found to be potent against hepapititas, AIDS & SARS7,8,9.Hydrazines derivatives occur naturally in tobacco and mushrooms,p-tolylhydrazine(bioactive molecule) isolated as a degradation product fromthe mushroom Agaricusbisporus, was found to be highly active compared to 5-flourouracil in vitro anticancer studies 10.
Diacylhydrazines have been identified as one of the most important types of insect regulators11-13. Several commercial compounds, such as tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide, chromafenozide,andhalofenozide, are all classified as diacylhydrazines, and all of these insecticides affect the ecdysonereceptor complex, leading to precocious lethal molting, especially in caterpillars 14,15.Diacylhydrazines have attracted significant attention because of their high insecticidal selectivity,simple structure, and low toxicity to vertebrates 13.
Aryl hydrazides and hydrazine compounds shows anticancer activity against 5 cancer cell lines namely A-549, SK-N-SH, HEP-2, PC-3 and MCF-7. Gallic acid hydrazide found to be most active,having high scores, indicating highest binding propensity towards the thymidylate synthase16.
Materials and Methods
All the reactions were carried out with A. R. grade chemicals. The C. P. grade chemicals, whenever used, were purified by standard methods. All m.p. were determined on a Yanaco micro-melting point apparatus andwere uncorrected. Elemental analysis was get done at CDRI Luckhnow. IR spectra were taken on a Perkin Elmer System 2000 FT-IR Spectrophotometer, in KBr pellets. EI-mass spectra were recorded on a VG Biotech Quattro 5022 spectrometer. 1H-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AMX-500 in CDCl3 and chemical shifts are given in ppm with TMS as internal standard .Silica gel was used for CC and silica gel 60 F-254 for TLC preparation. TLC optical rotations were measured using a Jasco DIP -370 Polarimeter in CHCl3.
Synthesis of Compounds
Alkyl,aryl and hetero aryl substituted hydrazine derivatives were synthesized.17-19
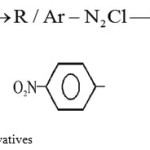 |
Scheme 1: Synthesis of Hydrazine Derivatives
|
Analysis
Table 1: physical characteristics and analytical data of the compounds investigated
| Compound | Colour | Molecular mass g/lmole | Elemental Analysis | Melting Point oC | Molecular formula | |||
| C% | H% | N% | O% | |||||
| 1 | Yellow Powder | 160 | 60 | 5 | 35 | 172.50 | C8H8N4 | |
| 2 | Orange-red needle shaped crystal | 153 | 47.05 | 4.5 | 27.4 | 20.9 | 156 | C6H7N3O2 |
| 3 | Clear Liquid | 136 | 70.5 | 8.8 | 20.5 | 22, B.P.74 | C8H12N2 | |
Table 2: IR spectral data of the compounds investigated in cm-1
|
Compound |
VN-H | VN-N | VC-H | VC-C | VC-N |
VC=N |
| 1 | 3304, 3411 | 1373 | 3000, 2976 | 1540, 1465 | 1289 | 1596, 1668 |
| 2 | 3322, 3202 | 1377 | 3087 | 1532, 1501 | 1341, 1315 | 1600, 1559 |
| 3 | 3405 | 1395 | 3020, 2850 | 1610, 1118 | 1310 |
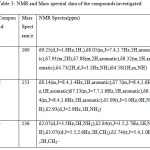 |
Table 3: NMR and Mass spectral data of the compounds investigated Click here to View table |
Biological Activity
All the synthesized compounds have been tested for theirbiological activity.
Compound 1 shows antihypertensive activity. It can be used to treat high blood pressure, which helps in preventing strokes, heart attacks and kidney problem. For thisNon-invasive (Tail cuff method) has been used.
Compound 2 shows anticancer activity against SK-N-SH (CNS) cancer cells.Thisactivity of the compounds have been test by MTT essay.
Compound 3 shows antidepressant activity. It is a non-selective momoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor commonly used to treat depression and panic disorder.It is checked by the behavioral despair test (porsolt –forced swimming test).
Results and Discussion
Compounds were synthesized from their respective amines. Synthesized compounds shows antihypertensive , antidepressant and anticarcinogenic activity.Compound 2 shows anticancer activity against SK-N-SH cancer cell line with IC50= 29µg/ml.
Aknowledgements
The author is thankful to Dr. Anil Gupta for their guidance in the research work and grateful to Govt. Dungar College Bikaner for providing facilities to carry out the work.
References
- Ragnarsson,U.Chemical Society Review,2001,30,205-213.
CrossRef - Ling, L.; Urichuk, L.J.; Sloley, B.D.; Coutts, R.T.; Baker, G.B.; Shan, J.J.; Pang, P.K.T. Bioorg.Med.Chem. Lett. 2001,11,2715-2717.
CrossRef - Černuchová, P.; Vo-Thanh, G; Milata, V.; Loupy, A; Jantová, S.; Theiszová M. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 5379-5387.
CrossRef - Abadi, A.H.;Eissa, A.A.H.; Hassan G.S.;Chem. Pharm. Bull.,2003,51,833-844 .
CrossRef - Abdel-Aal, M.T.; El-Sayed, W.A.; El-Ashry,E.H.;Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2006,339, 656-663.
CrossRef - Rabong,C.;Jordis,U.,;Phopase,J.B. J.Org.Chem.2010,75, 2492-2500.
CrossRef - Zhang, R.;Durbin,J.P.;Windsor,W.T.Biorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002,12,1005-1008.
CrossRef - Raja,A.;Lebbos,J.;Kirkpatrick,P.Nat. Reve. Drug.Discov.2003,2, 857-858.
CrossRef - Lee,T.W.;Cherney,M.M.;Huitema,C.L.J.;James,K.E.; et al. J.Mol.Bio. 2005,353, 1137-1151.
CrossRef - Chitra G, Investigation of chemical constitutents of Agaricusbisporus for anticancer activity , National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER) ,SAS Nagar, 2005.
- Wing, K.D. Science.,1988, 241, 467-469.
CrossRef - Sun, R.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, Q.S.; Song, H.B.; Huang, R.Q.; Bi, F.C.; Wang, Q.M.J. Agric. Food Chem.2009, 57, 3661-3668.
CrossRef - Wang, H.; Yang, Z.K.; Fan, Z.J.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Mi, N.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, Z.C.; Song,H.B.; Liu,F. J. Agric. Food Chem.2011,59, 628-634 .
CrossRef - Yanagi, M.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kawagishi, A. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006,31, 163-64.
CrossRef - Aguirre, O.U.; Martínez, A.M.; Campos-García, J.; Hernández, L.; Figueroa, J.I.; Lobit, P.; Viñuela, E.; Chavarrieta, J.M.; Smagghe, G.; Pineda1, S. Insect Sci. 2013,20, 734-742 .
CrossRef - Gohil,V.K.; AgrawalS.K.; Saxena,A.;Garg,D.;Gopimohan,C.; Bhutani,K.K.; Indian J. of Experimental Biology. 2010,48, 265-268 .
- Frahn,J.L.;Illman,R.J.Aust. J. Chem. 1974,27, 1361-1365.
CrossRef - Hunsberger,M.;Shaw,E.; Fugger,J.;Ketcham,R.; Lednicer,D.J. Org. Chem. ,1956,21, 394-399.
CrossRef - Khan,K.M.;Rasheed,M.;Ullah,Z.;Hayat,S.; Kaukab,F.;Choudhary,M.I., Atta-ur-RahmanandPerveen,S.Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry ,2003,11,1381-1387.
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









