Synthesis of 3-Bromo Flavones from 2-Hydroxy-3, 5-Dibromo-4’nitro Dibenzoyl Methane
R.E. Bhadange1 and R. P. Ganorkar2
1Department of Chemistry, ShriShivaji College, Akola - 444 101, India. 2Department of Chemistry, Mahatma FuleArts,Commerce and Sitaramji Chaudhari Science Mahavidyalaya, Warud Dist. Amravati - 444 906 India.
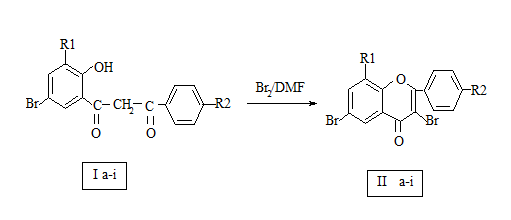
A new 3-bromo substituted flavones have been synthesized by the reaction of 2- hydroxy-3, 5-dibromo-4'nitro dibenzoyl methane was dissolved in dimethyl formamide (DMF) and pure bromine was added. The mixture was refluxed for 1-3 hours. Then cooled, diluted with ice-cold water and crystallized from alcohol-acetic acid mixture to get 2(4'nitrophenyl)-3,6, 8-tribromo flavones.The structures of all newly synthesized compounds were confirmed on the basis of IR,NMR. The melting points were taken in an open capillary tube.
KEYWORDS:Synthesis; Dibenzoyl methane; Bromo-Flavones
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Bhadange R. E, Ganorkar R. P. Synthesis of 3-Bromo Flavones from 2-Hydroxy-3, 5-Dibromo-4’nitro Dibenzoyl Methane. Orient J Chem 2012;28(3). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Bhadange R. E, Ganorkar R. P. Synthesis of 3-Bromo Flavones from 2-Hydroxy-3, 5-Dibromo-4’nitro Dibenzoyl Methane. Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=23175 |
Introduction:-
Flavones constitute large segment of natural products.Synthesis of flavones has attracted considerable attention due to their significant biocidal1-3, pharmaceutical 4-7anti- cancer8 and anti-inflammatory 9-10effects.Dibenzoyl methane reacts in DMF medium or with bromine in DMF to give 3-halo flavones11. 1, 3 diketones was transformed into 7-hydroxy-6-nitro flavone12.Some new biologically active chalcones and flavones have been synthesized 13.3-chloro flavones were prepared by action of thionyl chloride or sulphuryl chloride with flavones14-16. Antibacterial activity of some new chalconesand flavones having 2-chloro-8-methoxyquinolinyl moiety17.
The literature survey clearly indicates that 3-bromo substituted flavones are not yet synthesized. It was therefore thought of interest to synthesis 2(4’nitrophenyl)-3, 6, 8-tribromo flavones from 2- hydroxy-3, 5-dibromo-4‘nitro dibenzoylmethane(IIa). 2- hydroxy-3, 5-dibromo-4‘nitro dibenzoyl methane (0.01 moles) (Ia) was dissolved in dimethyl formamide (DMF) and pure Bromine (0.01 moles) was added. The mixture was refluxed for 1-3 hours. Then cooled, diluted with ice-cold water and crystallized from alcohol-acetic acid mixture to get 2(4’nitrophenyl)-3, 6, 8-tribromo flavones (IIa). Structures of these compounds have been established by spectral analysis.
EXPERIMENTAL:-
Melting point were taken in Silicon Oil bath instrument in open capillary and are uncorrected . Purity of the compounds was checked by TLC on silica gel G plates. IR spectra were recorded in Nujol, H1 NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3 with TMS as an internal standard.
Preparation of 2-(4′-nitrophenyl)-3,6-8-tribromo flavones (IIa):-
2- hydroxy-3, 5-dibromo-4‘nitro dibenzoyl methane (0.01 moles) was dissolved in dimethyl formamide (DMF) and pure Bromine (0.01 moles) was added. The mixture was refluxed for 1-3 hours. Then cooled, diluted with ice-cold water and crystallized from alcohol-acetic acid mixture to get 2(4’nitrophenyl)-3, 6, 8-tribromo flavones (IIa), m.p.-1690c.
It show negative ferric chloride solution test indicate the involvement of phenolic –OH group in cyclization.
Similarly other compounds (II a-i) were prepared by above method.
Scheme of Compounds (IIa-i)
Spectral interpretation of (2i)
IR spectrum was recorded in Nujol.
IR(υmax)cm-1 :-
- 1663 cm-1(C=0).
- 1590cm-1 (C=C).
- 1249 cm-1 (C-O-C )
- 702 cm-1 (-C-Br).
NMR :-
H PMR was recorded in CDCl3 with TMS as internal standard.
- 6.85-7.97 δ (m, 6H, Ar-H).
Physical data of synthesized 2-(4′-nitrophenyl)-3,6-8-tribromo
flavones (IIa)
|
Sr.No. |
compounds |
R1 |
R2 |
M.P(0C) |
Yields in % |
|
1 |
IIa |
Br |
NO2 |
111 |
60 |
|
2 |
IIb |
Br |
Cl |
178 |
76 |
|
3 |
IIc |
Br |
NH2 |
138 |
69 |
|
4 |
IId |
NO2 |
NO2 |
252 |
75 |
|
5 |
IIe |
NO2 |
Cl |
206 |
73 |
|
6 |
IIf |
NO2 |
NH2 |
131 |
80 |
|
7 |
IIg |
H |
NO2 |
293 |
78 |
|
8 |
IIh |
H |
Cl |
224 |
72 |
|
9 |
IIi |
H |
NH2 |
261 |
71 |
AKNOWLEDGEMENT:
The authors are thankful to Department of Chemistry ShriShivaji College Akola & Mahatma Fule Arts, Commerce And SitaramjiChaudhari Science Mahavidyalya, Warud for their valuable Support and necessary laboratory facilities during research work.
REFERENCES:-
- Rao K.V.,ChattopadhyayaS.K&Reddy G.C,J Agric Food Chem 38 ,1990,1427.
- Weidenborner M &Jha H.C ,PesticSci 38,1993,347.
- Silva A.M, Weidenborner M &Cavaleiro J.A S,Mycol Res 102 ,1998,638.
- Wu E S C,Loch J T ,Toder B H ,Borrelli A R ,Gawlak D ,Radov L A &Gensmantel N P ,J Med Chem 35,1992,3519.
- WolfmanC,Viola H, MarderM,WasowskiC,ArdenghiP,Izquierdo I ,Paladini A C &Medina J H, Eur J Pharmacol 318,1996,23.
- AkamaT,IshidaH,KimuraU,GomiK,SaitoH,FuseE,KobayashiS,Yoda N & Kasai M,J Med Chem 40,1997,1894.
- Gee J M &Johnson I T,Curr Med Chem 8,2001,1245.
- Leu Y I,Ho D K ,Cassady J M,Cook V M &Barid W M,J Nat Prod 55,1992,357.
- Fishkim R J & Winslow J T ,Psychopharmacology (Berl),132,1997,335.
- Dao T T,Chi Y S ,Kim J,Kim H P,Kim S & Park H,Bioorg Med ChemLett,14,2004,1165.
- BhadangeR. E., DoshiA. G. andRautA. W.Asian J. Chem.,14,509-511,(2002).
- WentaoGao,JianGui and Tianyu Zhuag,Molecules,9,842-848,(2004).
- MokleS. S., VibhuteY.B, DerPharmaChemica, 2009, 1(2): 145-152.
- MerchantJ. R andRegeD.V., Chem.Communication, 380, (1970).
- CamerF and ElshmgG., Ber, dt.Chem.Ges. 89, 1, (1956).
- MerchantJ. R., RegeD.V. andBhatA. R, Indian J.Chem.,10, 142,(1972).
- MokleS.S., KhansoleS.V, PatilR.B. And VibhuteY.B,Int. J. Pharma and Bio Sciences V1(1)2010

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.