A Recent Review on Chemistry and Biological Activities of Bryophyllum Pinatum (Lam.) Oken Family: Crassulaceae
Priyanka Yadav* , Arun Kumar Mishra and Harpreet Singh
, Arun Kumar Mishra and Harpreet Singh
Phytochemistry Research Laboratory, Faculty of Pharmacy, IFTM University, Moradabad, 244001, India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: priyankayadav22051986@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/370202
Article Received on : 13-02-2021
Article Accepted on :
Article Published : 03 Mar 2021
Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken belongs to the family Crassulaceae, one of the important medicinal plants which has great significances to treat various disorders, ailments in human beings. This study tells phytochemical constituents and pharmacological activities of extracts of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken. The aim of this review is to emphasise the recent and advanced research on different parts of plant extracts used. The forty secondary metabolites were isolated by different researchers where the most important includes flavonoids, terpenoids, glycosides, steroids and these secondary metabolites were responsible for various biological actions as antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, analgesics, wound healing and hepatoprotective actions which are incorporated. All this information gathered into this review were collected by using electronic search as PubMed, Research gate, Elsevier, Google scholar and Web science. Further studies also required on extracts for getting more information about mechanism of action, biological effects, safety, dosage required. By observing the medicinal uses and pharmacological profile of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken might be transferred into a new various herbal formulation and can report for future.
KEYWORDS:Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken; Chemical Constituents; Pharmacological activity; Physicochemical properties
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Yadav P, Mishra A. K, Singh H. A Recent Review on Chemistry And Biological Activities of Bryophyllum Pinatum (Lam.) Oken Family: Crassulaceae. Orient J Chem 2021;37(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Yadav P, Mishra A. K, Singh H. A Recent Review on Chemistry And Biological Activities of Bryophyllum Pinatum (Lam.) Oken Family: Crassulaceae. Orient J Chem 2021;37(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2PiUGuT |
Introduction
Our traditional medicinal system includes Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani. This Ayurveda concept emerged between 2500-500 BC in India (1). The factual meaning of Ayurveda is “science of long life” and by using different modern approaches, techniques the herbal products derived or in combination from medicinal plants used for diagnose and treat the illness (2). Mostly population of world depends on Traditional medicines (TM) for primary health care Now, the derived from herbal plants and herbal products has widely used (3).The market would be increased which cost around $five trillion in coming years by 2050 according to WHO. India is sitting on a gold mine of well-recorded and traditionally well-practiced knowledge of herbal medicine with rich culture and natural biodiversity which offers a unique opportunity for drug discovery researchers .Man tried to explore and utilise these natural substances for prevention the illness and betterment for mankind. The levels of drug resistance are increasing and difficulties of being able to afford high cost in poor areas due to such problems today, Traditional medicines (TM) now became the roots of beneficial source of treatment. The use of ethno-botanical preparations for various reasons, is still continued by various cultures all around the world. They may be the oldest “evidence-based Medicine” (4). Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken belongs to family of Crassulaceae which is a perennial herb commonly known as Paranbija, Patharchatta and Pashanbheda means stones dissolvers according to Ayurveda (Figure 1) (5). Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken is derived from Greek word Bryo means to sprout and phyllon means leaf and pinnatum is the Latin adjective (adj.) word which has meaning “winged, pinnate” (6,7). This plant is fleshy upright and succulent plant usually growing at about 60-120 cm tall. The drooping bell shaped flowers are greenish-yellow to pinkish-red in colour up to 7 cm long. The leaves are oppositely arranged with three or five leaflets and reproduction done by seeds or by leaf buds (8, 9). This family consisting 25 genus and around 425 species and the figure of plant is shown in Figure1 This plant can be known by various names as Cotyledon calycina, Cotyledon calyculata, Cotyledon calyculata, Cotyledonpinnata, Kalanchoe pinnata(11) and the vernacular name of this plant are Pashanabheda in Sanskrit, Air plant in English, Patharchatta in Hindi, Patharkuch in Bengali (6). This miracle plant which is cultivated widely in America, China, India and Australia. It can be lined in to its popularity as house/garden plant due to its naturalisation of this plant and grows all over India in hot and moist areas, inhabiting warm and temperate climates from sea level to 8500ft and regarded as an invasive species. It is grown as a house ornament plant (11, 10). It is having folklore uses mainly as carminatives, haemostatic, astringent, wounds, boils, burns, menstrual pain, haemorrhage, scalds and diarrhoea and tonic . The leaves and leaf juice of the plant were used historically as antipyretic, antimicrobial, medicament, antitumor, inhibitor, antiulcer, medicament, astringent, antiseptic, antilithiatic and cough summarised in Table 2 (12, 13). According to phytochemical studies the plants contained various secondary metabolites as steroids, alkaloid, flavonoids, phenols, tannins, bufadienolides and some acids which are responsible for various pharmacological actions mentioned in Table 1 (12) and having high therapeutic value (10). Various medicinal plants have their similar species by their genus so it will get difficult to understand their activity and their identity. Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken also similar to lavender scallops Bryophyllum fedtschenkoi and Bryophyllum delagoense, hybrid mother of millions of millions Bryophyllum x houghtonii, mother-of-thousands Bryophyllum daigremontianum. These species can be distinguished by macroscopic and microscopic characters as discussed below.
Botanical Description
Macroscopic Characters
The young roots are greenish brown in colour with tap root type of 7-10 cm long and light brownish colour of old roots. The powdered roots having sweetish taste and pleasant odour (14, 15). Leaves are simple, succulent, opposite, dark green in colour with 10-12 cm long and light green streaked in middle, pointed long petiole, asymmetric base, apex is obtuse. some leaves which are at upper side consisting 3-4 foliates with characteristic odour and bitter taste (15). The leaf furnished buds on its structure which can give rise to a new plant. The stem is rough with lenticels in its skin with pleasant odour. Flowers are pale yellow in colour, streaking with redness, corolla 3-5cm long cymes are paniculate, each flower produce on a stalk, 10-25 mm long. They have prominent, inflated, yellowish-green coloured sepals 25-55 mm long that are partially fused into a calyx tube. Seeds are numerous and obovoid. The fruits seeds are in brown colour having, 1mm long. Each fruit is covered with four carpels. The fruits are pappery and membranous with 15 mm long. The ovary has four carpels, slightly fused together in the center, with slender styles (16).
Microscopic Characters
The adaxial side is broadly shallow and convexed by abaxial side. It consists a thin adaxial epidermal layer and an abaxial layer both with less distinct cells which are circular and compact form and contained thick xylem band spreaded horizontally in a diffused way (14), broad midribs with upper and lower epidermis and showing spongy parenchymatous features, conjoint chlorophyll with two vascular bundles. The roots are in circular structure followed by thin inner cortex and outer cortex. The Outer cortex having 3-4 thick wall layered consisting of sclerenchyma cells. Thin walled Inner cortex made up of spongy cells i.e. parenchymatous with engulfed starch grains. The centre of roots filled with parenchymatous pith contained starch grains. Petiole having single layered which is in circular structure (15).
Botanical Classification (11)
Kingdom Plantae
Subkingdom Tracheobionta
Division Spermatophyta
Subdivision Magnoloiphyta
Class Mangnoliopsida
Subclass Rosidae
Order Saxifragales
Family Crassulaceae
 |
Figure 1: Bryophylum pinnatum Lam. (Oken) |
Physicochemical properties
As literature surveyed, the physiochemical properties of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken were observed in the following values (17) Total ash, Acid insoluble ash, Water soluble extractive value, Alcohol soluble extractive value were found to be as 5.1% 1.69%, water soluble ash 4.19%, 19.80%, 5.60% respectively (14,15)
Chemical Constituents (18,19) This divine plant contains various active constituents which are responsible for pharmacological activities which are described below. The steroids as stigmasterols and bufadienolides were found or screened out from the shoots and dried leaves Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken by using dichloromethane (DCM) solvents and methanol for extraction respectively which all are shown as in Table 1 . The extracts of leaves, roots, stem and others aerial parts of plant constituted alkaloids, tannins, anthocyanins, glycosides as kaempferol di-glycoside, kapinnatoside (8), bufadienolides, saponins, quninines, Phenols and Phenylpropanoids1 as syringic acida ,caffeic acidb vanillic acidc, cinnamic acidd, 4-hydroxybenzoicacid (HBA), p-hydroxycinnamic acide, ferulic acidf, coumaric acid,para coumaric acidg, catechuic acid, protocatechuic acidh, phosphoenolpyruvatei (20), Flavonoids2 as astragalinj, luteolink, rutinl, kaempferolm quercetin, quercetin-3L-rhamonsido-L-arabino furanoside, quercitrino, flavonesn, quercetin-3-O-diarabinoside, kaempferol-3-glucoside, apigeninoo(21,22) Cardenolide and Steroidal constituents3 as β-sitosterol, bryophyllol, bryophynol, bryophyllin Bp, bryophyllin Aq, bufadienolide, bersaldegenin-3-acetate, bryotoxin A, bryotoxin B, bersaldegenin-1, 3, 5-orthoacetater (23) Triterpenoids4 as α-amyrins, β-amyrin, amyrinacetatet, bryophollenone, bryophollone, taraxerolu, pseudo taraxasterolv, glutinolw (21, 22, 24) andFatty acid5 as palmitic acidx, stearic acidy, traces of arachidicz and behenic acid and by GC-MS chromatogram observed 6 peaks indicating acids are Hexadecenoic acid, methyl ester, 9,12-Octadecanoic acid, Octadecenoic acidzzz, methyl ester, Linoleic acid ethyl ester where fatty acid was major constituted (25). This miracle plant is also good source of carbohydrates, proteins, iodine and Sugar6 contents too such as raffinosez1, lactosez2, sucrosez3, glucosez4, galactose, fructose and also various hydrocarbons like as alkanes having carbon C24-35, alkanols having carbon C27-34 (11). The aerial parts of this plant are rich in Macro elements7 including calcium, potassium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorous and Microelements8 including zinc, vitamins are tocopherolz5, ascorbic acidz7, thiamine, riboflavinz6, niacinz8, pyridoxinez9, glycinez10, cysteine (6). By the hydro-distillation of leaves of this Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken yielded essential oil which constituted nineteen compounds determined by GC/MS contained oxygenated hydrocarbons, oxygenated monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, oxygenated sesquiterpenes, curcumin, caryophyllene, octen-3-ol. It also possessed bufadienolides as bryophyllin A, bryophyllin B and bryophyllin C which were also isolated from this Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken plant and reported it as insecticidal properties (23). The leaves also contained chalcones, aurones, anthocyanidin.
Table 1: Phytocompounds isolated from Bryophllum pinnatum (lam.) Oken.
|
Category |
Compounds isolated |
Part plant |
References |
|
1Phenol, phenylpropanoids |
Syringic acida |
Aerial parts |
Gaind et al., 1974; Costa et al; 1995 |
|
|
Caffeic acidb Vanillic acidc Cinammic acidd P-coumaric acidg p-hydroxy cinnamic acide Ferulic acidf Protocatechuic acidh Phosphoenolpyuruvic acid i |
|
|
|
2Flavonoids |
Astragalinj |
Leaves |
Shazid et al., 2012; Simplice et al. ,2012 |
|
|
3,8dimethyl-4,5,7 trihydroxyflavone Rutinl luteolink Kaempferolm Quercetin flavonesn Quercetrino, Apigeninoo Quercetin-3-o-diarabinoside Quercetin-3-l-rhamnosido-l-arabino-furanoside Kaempferol-3-glucoside-7-o-D-glucopyranoside |
|
|
|
3Steroids
|
Bryophyllin Aq Bryophyllin Bp Bryophyllin C bersaldegenin-1, 3, 5-orthoacetater Stigmast-24-enol (24S)-stigmast-25-enol 25-metylergost-24(28)-enol (24R)-ergost-5-enol (24R)-stigmast-5-enol, stigmast-7,24-dienol (24S)-ergosta-5,25-dienol, (22E,24S)-stigmast-5,22-dienol, stigmast-5,24-dienol (24Z)-stigmast-5,24(28)-dienol,(24R)-stigmast-5,25-dienol (24S)-stigmast-5,25-dienol 25-metylergost-5,24(28)-dienol
|
Leaves
shoots
|
Akinpelu et al., 2000; Kamboj et al., 2009
Akhisia et al., 1991
|
|
4Triterpenoid |
Amyrins Beta amyrinu amyrin acetatet Glutinolw Taraxasterolv Taraxeroluu |
Aerial part |
Khushboo et al.,2009; Akinpelu et al.,2000 |
|
5Fatty acids |
palmitic acidx, octadecanoic acidzzz stearic acidy, arachidic acidz, behenic acidzz, |
Fresh leaves |
Orisakeye et al.,2015 |
|
6Sugars
7Macroelements |
Raffinosez1 Lactosez2 Sucrosez3 Glucosez4
Sodium, Zinc, Calcium |
Leaves
Aerial parts |
Toshioro et al.,1991; Pattewar et al.,2018
Thorat et al., 2017 |
|
8 Microelements
|
vitamins- Tocopherolz5, Riboflavinz6 Ascorbic acidz7, Niacinz8,pyridoxinez9, glycinez10 |
Aerial parts |
Thorat et al.,2017 |
a-4-Hydroxy – 3, 5 – dimethoxy benzoic acid
b-1,3,7-trimethylpurine-2,6-dione
c-4-hydroxy- 3- methoxy benzoic acid
d-2(E)-3-Phenylprop-2-enoic acid
e-4,4,6a,6b,8a,12,14b-heptamethyl-11-methylidene-docosahydropicen-3-ol
f-(E)-3-(4-hhydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) Prop-2-enoic acid
g- 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) prop-2-enoic acid
h-3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
i-2-(phosphonooxy)acrylic acid
j- 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl) oxan-2-yl] oxychromen-4-one
k-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-chromenol
l- 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy]-4H-chromen-4-one
m- 3,4,5,7-tetrahydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one
n-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-triihydroxy-4-chromen-4-one
0-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7- dihydroxy-3- [ [(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)- 3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-2- tetrahydropyran] oxy]-4-chromenone
00-5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
p-[(1R,6R,11R,14S,16S,18R)-10,14,18-trihydroxy-6-methyl-2-oxo-7-(6-oxopyran-3-yl)-3-oxapentacyclo [9.7.1.01,14.04,19.06,10] nonadecan-16-yl] acetate
q- (1S,4R,5S,8R,9R,11R,12S,13R,14R,16R,18S)-5,11-dihydroxy-9,16-dimethyl-8-(6-oxopyran-3-yl)-15,17,20-trioxahexacyclo [14.3.1.114,18.01,13.04,12.05,9] henicosane-13-carbaldehyde
r-5-hydroxy-9,16-dimethyl-8-(6-oxopyran-3-yl)-15,17,20-trioxahexacyclo [14.3.1.114,18.01,13. o4,12.05,9] henicosane-13-carbaldehyde
s-(3β)-Urs-12-en-3-ol
t-(4,4,6a,6b,8a,11,12,14b-octamethyl-2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydro-1H-picen-3-yl) acetate
u-(3β)-Olean-12-en-3-ol
uu- (3S,4aR,6aR,6aS,8aR,12aR,14aR,14bR)-4,4,6a,6a,8a,11,11,14b-Octamethyl-1,2,3,4a,5,6,8,9,10,12,12a,13,14,14a-tetradecahydropicene-3-ol
v-(3S,4aR,6aR,6aR,6bR,8aR,12S,12aR,14aR,14bR)-4,4,6a,6b,8a,12,14b-heptamethyl-11-methylidene-1,2,3,4a,5,6a,7,8,9,10,12,12a,13,14,14a-hexadecahydropicen-3-ol
w-(3S,6aS,6aS,6bR,8aR,12aR,14aR,14bS)-4,4,6a,6b,8a,11,11,14a-octamethyl-1,2,3,6,6a,7,8,9,10,12,12a,13,14,14b-tetradecahydropicen-3-ol
x- hexadecenoic acid
y-(Z)-Octadec-9-enoic acid
z-(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid
zz- Docosanoic Acid
zzz- Octadecenoic acid
z1-(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy -6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane-3,4,5-triol
z2- Beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 arrow4)-D-glucose
z3-Beta-D-fructofuranosyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside
z4-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal
z5-(2R)-2,5,7,8-Tereamethy-2[(4R, 8R) -(4.8.12-trimethyltridecy)] chorman-6-ol
z6-7,8-Dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl] benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione
z7-(5R)-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5H)-one
z8-Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid
z9-4,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylpyridin-3-ol
z10-2-Aminoethanoic acid
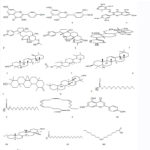 |
Figure 2: Chemical structures of following active compounds. Click here to View figure |
Pharmacological Activity
Antidiabetic Activity (6)
Flavonoids and alkaloids were highly found when compared to steroids and terpenoids which were present in little while glycosides and reducing sugar were present moderately performed on rats. The ethanol extracts of T. africana leaves and Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken plants mixture with an equal amount and administered to albino rats to each three groups for 21 days. The different ratios of mixture of above plant extracts given to the groups and analysed their Plasma sugar contents, glycaemic status and serum lipid profiles of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats from the blood of tail vein at various 30, 60 and 120 minutes
intervals which showedsignificant reduction (P 0.05) by STZ-induced diabetes glucose levels, density compound protein level and increase in high density compound protein level (26, 27). The medicinal drug activity conjointly investigated of Bry.pin(Lam.) Lorenz Okenfuss plant’s leaf liquid extract in rats, victimization contemporary egg albumin-induced pedal and streptozotocin STZ induced diabetes mellitus then this plant extract 25–800 mg/kg p.o. which also caused significant (P < 0.05–0.001) hypoglycaemia in rats. Thus, results of this animal study suggested Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken leaf aqueous extract possess micronutrient i.e. zinc which possessed hypoglycaemic activity (28).
Hepatoprotective Activity
Liver is the important and largest organ in the vertebrates which detoxifies the toxins from body and helping in metabolism of body. By the chemicals and drugs used harmed the liver organ and its metabolism. Various medicinal plants used for treatment liver problems similarly, ethanolic extracts of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken leaves also experimented on rats for liver cirrhosis, liver cancer and liver diseases. According to researchers, the aqueous and ethanolic extract of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken in the doses of 250 and 500 mg/ kg orally given to those rats which having injuries by induced N-diethyl nitrosamine which has showed a significant liver protection (10). Other findings that the juice of the leaves of B. pinnatum and the ethanolic extract of the marc which was left behind after squeezing that juice also found hepatoprotective action against CCl4-induced liver disorder. It showed hepatoprotective action as observed in vitro and in vivo. The expressed juice was more found to be hepatoprotective than the ethanolic extract (EE) of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken .
Antileishmanial Activity (6)
Leishmania’s is caused by parasite of leishmania type. It is spread by various type of sand-flies. The symptoms are skin ulcers, high fever and enlarged liver. This infection now became worldwide health problem majorly in developing countries. The incidence of the emergence of this disease has increased various health issues. So, there is an emergency requirement for effective drugs which can replace those current drugs in use (28). According to phytochemical studies Some flavonoids like as quercetin and its rhamonsyl part which shows pharmacological activity. The quercetin, quercitrin, azelin were extracted from the plant showed antileishmanial activity (18) which acted their preventive action against amazonensis amastigotes by activation of nitrogen intermediates pathway-2 macrophages. The preventive effect of plant in leishmaniasis may not be due to a direct effect on the parasite itself but rather activation of the reactive nitrogen intermediates pathway of macrophages (30).
Urolithiatic Activity
These are clumps of mineral that accumulate on inner lining of kidney. Symptoms are- dark colour urine, frequent urination, pain during urine, lower abdominal pain. According to Ayurveda this plant is also called stone dissolver. The extracts of leaf part of plant were exhibited to show the preventive effects on urolithiasis through dissolution of formed stones and through combating the formation of calcium oxalate crystals. There was decrease in body weight and increased in rest urinary parameters such as uric acid, creatinine, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium and in serum biochemical parameters also (creatinine, uric acid, urea, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium) due to induction of lithiatic on rat kidney by ethylene glycol in drinking water. Due to presence of flavonoids, phenolic compounds, saponins and steroids in the alcohol extracts of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken which were responsible for urolithiasis activity (31). When this alcohol extract (alc) treated with Ethylene glycol (EG)-induced observed a sudden decrease serum biochemical and other urinary parameter and it decrease the urine volume, pH, magnesium and creatinine clearance, oxidative and histological damages. Some other researchers also reported in-vitro inhibitory activity of the leaves of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken plant on lithiatic (32).
Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Activity
Analgesics relieves pain by acting in CNS on peripheral pain mechanism without altering consciousness. Some steroids derivatives are also phytoconstituents of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken which were isolated from leaves of the plant and to be active in red inflammation which showed percentage (%) inhibition 87.29 and 84.45 when compared with Diclofenac, standard drug towards carrageenan induced paw oedema model and acetic acid induced model respectively (33). Similarly, it showed analgesic activity by acetic acid induced writhing test i.e. 75.72% in mice. So, the (%I) inhibition and (%P) protection against above mentioned models expressed their analgesic activity and anti-inflammatory of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken due to the presence of steroidal compound.Some other research done where pain induced by chemically and thermally in experimental animals which were performed on rats to evaluate the analgesic activity against fresh egg albumin. The aqueous extract of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken given to induced rats at 25-800 mg/kg showed protective effects (35).
Immunomodulatory Activity
The aqueous extract of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken as found to be inhibits mast cells activation and anaphylactic reaction and help in preventing allergic airway disease treated in vitro/vivo which gave a new light to immunomodulators functions (6). There is another finding regarding immunomodulator activity where Lou M rats were used for experiment with parameters eosinophil count, cytokinin production, T-cell proliferation, histamine release assay were observed against anaphylactic shock (36; 35).
Antioxidant Activity
The leaf extract showed antioxidant action when it was performed on rats produced a concentration dependent increase in percentage antioxidant activity in DPPH radical scavenging activity. The optimum antioxidant activity of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken extract was produced at 400 μg/ml concentration when compared with ascorbic acid and observe value of P<0.005 (38). The Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken extract produced increased antioxidant activity in Ferric reducing antioxidant power compared with ascorbic acid (P<0.005) at 400μg/ml concentration (33). The oxidative activity of Bry.pin(Lam.) Okenleaf extract was evaluated by DPPH and nitric oxide (NO) free radical scavenging models which showed 50% inhibition at 144.23 μg/ml concentration with aqueous extract and showed inhibition at concentration 117.42 μg/ml with alcoholic extract too. Similarly, other model of antioxidant Nitric oxide scavenging also showed 50% inhibition with both aqueous and alcoholic extract (34).
Wound healing Activity
Wound healing is the process of healings the wounds and repairing the cuts and damaged skin layer by increasing the production of collagen and then epidermis tissues are regenerated. The stages for the process of wound healing inflammation, proliferation, remodelling. This activity shown by the water extract of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken through the excision and incision model. This model gave a significant decrease in the epithelization period and scar area. The scar area was reduced with water extract up to (30.50 ± 0.84) treated group as compared to control group (43.66 ± 2.05) (p<0.001), So the result was production of collagen and granulation of tissues increased with the water extract of the leaf part when it was compared to control group of rats (39). The three extracts of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken leaf of petroleum ether (PE), water and alcohol were given to treated groups for evaluation wound healing action which showed increasing the breaking strength of incision wounds as compared to manage teams of rats within the dose of every four hundred mg/kg orally on healing of excision wound, re-sutured incision and dead area wound models in unusual person rats (10). By investigation victimisation excision wound model in rats the ethanolic leaf extract expressed wound healing activity because of steroidal constituents
Antibacterial Activity
Various medicinal plants were used for antibacterial activity. The different extracts of leaf (methanol, water, local solvents) got lyophilized and juice of Bry.pin(lam.) Oken both have been shown its activity towardsGram-negative organisms like Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Escherichia coli, bacteria genus aeruginosa, enterobacteria flexneri and gram-positive organism like coccus aureus ATCC 25213, coccus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis and a plant life by victimisation Agar well diffusion and broth dilution strategies to guage the minimum repressing concentration (MIC) and minimum germicidal concentration (MBC) at 512 mg/ml to 4 mg/ml concentration This activity turned against for skin infection and could formulated into skin soaps.
Anticancer Activity
The carcinoma was induced to specific group of experimental rats and these treated groups of animals were evaluated by given methanol (meth) and aqueous extracts (aq) of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken with at doses of 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight i.p. once a day for 7 days continuously after 24 hour of cancer growth. The result was decreasing in tumour cell count and its weight (wt.) seen with the extracts treated group (41). This result was dose dependent and showed antitumor activity towards Ehrlich ascites carcinoma due to the presence of bufadienolides (42,43).
Neuropharmacological Activity
According to the studies the steroids (bufadienolides) and water-soluble constituents phytoconstituents present in this plant which were showing activity towards CNS depressants (44). The sedation activity proposed by treated with 50-200 mg/kg aqueous leaf extract of Bry.pin(Lam.) Okenin treated mice which was found to be in decreasing exploratory / locomotor activity and gave a marked of sedative effects with a dose dependent way. The results of reduction pentobarbitone induced sleeping time and minimised the rate of strychnine and picrotoxin which induced seizures respectively. These studies showed the potential of Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken extracts to give neuropharmacological activity on the central nervous system (45,10).
Table 2: Pharmacological Activity.
|
Pharmacological activity |
Extracts |
Parts used |
Type |
Mechanism of action (MOA) |
Models Used |
References |
|
Antidiabetic activity |
aqueous, ethanolic |
Leaves |
in vitro |
showed preventive effects towards blood glucose level |
Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced; Diabetes Mellitus |
Thorat et al., 2017; Ojewole et al., 2005 |
|
Hepatoprotective Activity
|
aqueous, ethanolic |
Fresh leaves |
In vitro/in vivo |
This extract lowered the enzymes SGOT, SGPT, SALP and SBLN which increased during liver disorder and involved antioxidant and oxidative radical scavenging action |
CCL4 induced Liver disorder |
Devbhuti et al., 2000; |
|
Urolithiasis activity
|
Alcoholic |
Leaf |
In vitro |
showed the preventive effects through dissolution of formed stones and through combating the formation of calcium oxalate crystals and showed decrease in body weight and increased in rest urinary parameters. |
Ethylene glycol Induced lithiasis on rats |
Yadav et al., 2016 |
|
Anti-inflammatory Actions
|
Aqueous |
Leaves |
in vitro |
by inhibition the release of histamine and cytokinin formation |
Carrageenan Induced Edema Model |
Quazi et al., 2011 |
|
Analgesics actions
|
Aqueous |
Leaves |
In vitro |
by acting in CNS on peripheral pain mechanism and relieve from pain |
thermal method; chemical methods |
Quazi et al., 2011 |
|
Antimicrobial Actions
|
aqueous, methanolic |
Leaf |
In vitro |
Showed bactericidal action against gram positive and gram-negative strains And showed action against fungus too by using models |
Agar well Diffusion Method Broth dilution method |
Aibinu, Akinsulire et al., 2007 |
|
Neuropharmacological actions
|
Aqueous |
Leaves |
in vitro |
Involved loss of coordination, CNS depressant actions and showed in decreasing locomotor’s activity during test |
Clinching, Climbing inclination Test model |
Salahdeen et al., 2006 |
|
Antinociceptive actions |
methanol, aqueous |
Leaf |
In vitro |
Inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin, cytokinin, histamine release |
hot-plate and acetic acid induced model |
Ojewole JAO., 2005 |
Side Effects and Toxicity
The leaf extract of this Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken plant contains not only flavonoids phenolic compounds, glycoside but this plant also possesses phenanthrene and bufadienolides which are toxic compounds and caused cardiac arrhythmia to the cattles after grazing Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken for 48 hours (46, 47).
Conclusion and Future perspectives
Since the early days of humankind, the plants, herbs and botanical garden are used throughout the world for cure and prevention of disease. About 25% of drugs which are prescribed all over the world are derived from the plants. The previous literature and present studies of Bry.pin(Lam.) oken showed leaves and roots were consisting terpenoids, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, steroids vitamins and some acids which would be a great help in new drug manufacturing for treatment of diseases. This plant grows majorly in the wild areas So, it is very important to conserve this medicinal plant which is known as miracle plant i.e. Bry.pin(Lam.) Oken and examined for their medicinal properties like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, urolithiatic and hepatoprotective property. In Odisha this plant known with the name of Basampatri are used in prevention to flatulence and in prevention of cough with ghee or garlic. People of Nigerians used filtrate of the leaves of plant in prevention of Asthma too. Though this plant showed some toxicity due to presence of bufadienolides which caused cardiac arrhythmia but only in cattles. So, it would be important to explore more of its species regarding their active constituents with their potential. Thus, we hope phytochemical studies and pharmacological properties helps and attracts the researchers in order to do new drug discovery and isolate, identify or characterise the structure of different active compounds which are responsible for activities. The pharmaceutical industries should adapt innovative step and necessary evidence for rational use of the plant as potent herbal medicine.
Acknowledgement
None
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest regarding this article.
References
- Subhose V P, Srinivas and Narayana A (2005) Basic principles of pharmaceutical science in Ayurveda. Bulletin Ind Instt Hist Med 35(2): 83–92.
- Ravishankar B and Shukla VJ (2007) Indian Systems of Medicine: A Brief Profile.Afr J Trad Comp Alter Med 4(3): 319–337.
CrossRef - Mukherjee PK and Wahile A (2006) Integrated approaches towards drug development from Ayurveda and other Indian system of medicines. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 103(1): 25-35.
CrossRef - Benbott A, Bahri L, Boubendir A and Yahia A (2013) Study of the chemical components of Peganum harmala and evaluation of acute toxicity of alkaloids extracted in the wistar albino mice. J Mat Env Sci 4(4): 558-565.
- Yadav M, Gulkari VD and Wanjari MM (2016) Bry.pinleaf extract prevent formation of renal calculi in lithiatic rats. Anc Sci life 36(2): 90-97.
CrossRef - Sheela S Thorat, Shah RR, Mohite SA and Patel NR (2017) A review of Bryophyllum pinnatum. Inter Res J Pharm 8 (12): 1-3.
CrossRef - Taylor L (2005) The healing power of rainforest herbs. A guide to understanding and using herbal medicinals. Sq One pub.
- Okwu DE, Uchenna DF (2009) Exotic multifaceted medicinal plants of drugs and pharmaceutical industries. African Journal of Biotechnology Vol 8(25): 7271-7282.
- Kamboj A and Saluja AK (2009) Bry.pin(Lam.) Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile: A Review. Pharm Rev 3(6): 364-374.
- Nagaratra A and Hedge PL (2015) A comprehensive review on Bryophyllum pinnatum. Journal of medicinal plants studies 3(5): 166-171.
- Pattewar SV et al., Kalanchoe pinnata: Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile. International Journal of Pharmaceutical science and Research. 2012. 3(4): 9931000.
CrossRef - Sheela S Thorat et al. A review of Bryophyllum pinnatum. International Research Journal of Pharm. 2017. 8 (12).
CrossRef - Mensor LL, Menezes FS, Leitão GG, Reis AS, dos Santos TC (2001) Screening of 0Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Photother Res 15(2):127-130.
CrossRef - Eboka JC, Ozoluaa RI, Durua CN and Uwaya DO (2010) Effects of aqueous leaf extract of Bry.pinon guinea pig tracheal ring contractility. Nig J Phys Sci (25): 149-157.
- Shah DP, Patel NM and Jain VC (2008) Microscopical and Preliminary Phytochemical Studies on Leaves of Bryophyllum calycinum Salisb.J Pharm Res 1(2): 230-232.
- Sharma A and Chandra N (2014) Pharmacognostic studies of Bryophyllum pinnatum. Pharmacog J Vol 6(6): 20-22.
CrossRef - Batygina T. B, Bragina E. A, Titova G. E (1996) Morphogenesis of propagules in viviparous species Bryophyllum daigremontianum and B. calycinum. Acta Soc Botan Polo 65: 127-133.
CrossRef - Devbhuti D and Gupta JK (2008) Phytochemical and acute toxicity study on B. calycinum. Acta P Pharmaceutica Deuy research 65(4): 501-504.
CrossRef - Kamboj A.K. Saluja et al., Bry.pin(Lam.) Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile: A Review. Pharmacognosy Review. 2009. Vol 3. no. 6: 364-374.
CrossRef - Kawade M, Ghiware NB, Ghante MH, Malwatkar SM, Vadvalkar SM, Dhadwe AK, Choudhary RV (2014) A review on Pharmacognostical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Potentials of Kalanchoe Pinnata. Am J Pharm Tech Res 4(1): 1-14.
CrossRef - Gaind KN and Gupta RL (1974) Identification of Waxes from the Leaves of Kalanchoe pinnata. Planta Med J 23: 193-197.
CrossRef - Shazid M. Sharker, Haque MR, Hossain MK and Chowdhury A (2012) Chemical and biological studies of Kalanchoe pinnata (Lam.) growing in Bangladesh. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed2(3): 1317-1322.
CrossRef - Simplice JN Tatsimo, Tamokou J D, Havyarimana L, Csupor D, Forgo P, Hohmann J, Kuiate JR and Tane P (2012) Antimicrobial and Antioxidant activity of kaempferol rhamnoside derivatives from Bryophyllum pinnatum. BMC Res Notes 5: 158.
CrossRef - Supratman U, Fujita T, Akiyama K and Hayashi H (2000) New insecticidal bufadienolides: bryophyllin C from Kalanchoe pinnata. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemistry 64(6): 1310-1312.
CrossRef - Akinpelu DA (2000) Antimicrobial activity of Bry.pinleaves. Fitoterp 71 (2): 193-194.
CrossRef - Orisakeye OT, Oladoye SO, Peters OA (2015) Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Bry.pinRoot. Nat P Chem Res 3(3):173.
CrossRef - Aransiola EF, Daramola MO, Iwalewa EO, Seluwa AM, Olufowobi OO (2014) Anti-Diabetic Effect of Bry.pinLeaves. Inter J Biotech Bioeng (8) 1: 89-91.
- Snafi AE (2013) The Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Bryophyllum calycinum. J Pharma Sci Res 4 (12): 170-176.
- Ojewole JAO (2005) Antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic effects of Bry.pin(Crassulaceae) leaf aqueous extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 99(1): 13-19.
CrossRef - Rocha LG, Almeida JRGS, Macedo RO and Barbosa-Filho JM (2005) A review of natural products with antileishmanial activity. Phytomed 12(6-7): 514-535.
CrossRef - Muzitano MF, Cruz EA, Almeida AP, Silva SAG, Kaiser CR, Guette C, Rossi-Bergmann B and Costa SS (2006) Quercitrin: an antileishmanial flavonoid glycoside from Kalanchoe pinnata. Planta Med (72): 81–83
CrossRef - Yadav Mahendra et al., Bry.pinleaf extract prevent formation of renal calculi in lithiatic rats., Ancient science of life. 2016. 36(2): 90-97.
CrossRef - Yasir F and Waqar MA (2011) Effect of indigenous plant extracts on calcium oxalate crystallization having a role in urolithiasis. Urol Res 39(5): 345–350.
CrossRef - Afzal M Gupta G, Kazmi I, Rahman M, Afzal O, Alam J, Hakeem KR, Pravez M, Gupta R, Anwar F (2012) Anti-Inflamatory and Analgestic Potential of a Novel Steroidal Derivative from Bryophyllum pinnatum. Fitoterapia 8 (5): 853-858.
CrossRef - Al-Snafi AE., The Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Bryophyllum calycinum. Journal of Pharma Sciences and Research. 2013. (12): 171.
- Quazi M, Sayyed N, Sheikh S, Gomase P and Choudhari A (2011) Phytochemical analysis of chloroform extract of roots of Kalanchoe pinnata by hplc and gcms. Inter J Pharma Sci Res 2(7): 1693-1699.
- Cruz EA, Da-Silva SAG, Muzitano MF, Silva PMR, Costa SS, Rossi-Bergmann B (2008) Immunomodulatory pre-treatment with Kalanchoe pinnata extract and its quercitrin flavonoid effectively protects mice against fatal anaphylactic shock. Int Immunopharm 8(12): 1616 –1621.
CrossRef - Samuel O, Ginika Q. Ihejirika,Oluchi N. Nwankudu, Yusuf N. Omeh and Maxwell Ezeja (2018) Antidiarrheal and Antioxidant activities of Methanol extract of Bry.pinleaf harvested from Southern Eastern Nigeria in mice. J Pharma Article ID 6810620: 6 pages.
CrossRef - Khan M, Patil PA and Shobha JC (2004) Influence of Bry.pin(Lam.) leaf extract on wound healing in albino rats. J Nat Rem 4(1): 41-46.
- Nayak BS, Marshall JR and Isitor G (2010) Wound healing potential of ethanolic extract of Kalanchoe pinnata Lam. leaf-A preliminary study. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology 48: 572-576.
- Shukla S, Pandey, G Mugesh , Das BC, Bharti AC, Maru S and Mahata S (2012) Anticancer property of bryophyllum pinnata (lam.) oken leaf on human cervical cancer cells. BMC comp alter med 12:15.
CrossRef - Supratman U, Fujita T, Akiyama K, Hayashi H., New insecticidal bufadienolides: bryophyllin C from Kalanchoe pinnata. Bioscience Biotechnology Biochemistry. 2000. 64: 1310-1312.
CrossRef - DevbhutiD, GuptaJ.K., Phytochemical and acute toxicity study on B. calycinum. Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica Deuy research. 2008. 65(4): 501-504.
- Fujimori HMD (1965) Potentiation of barbital hypnosis as an evaluation method for CNS depressant.Psychopharmac 7: 74–378.
CrossRef - Salahdeen HM, Yemitan OK (2006) Neuropharmacological effects of aqueous leaf extract of Bry.pinin mice. African Journal of Biomedicine Research 9: 101-107.
CrossRef - McKenzie RA and Dunster PJ (1986) Bryophyllum poisoning of cattle. Aust Vet J 63(7): 222-227.
CrossRef - Kolodziejczyk Czepas J and Stochmal A (2017) Bufadienolides of Kalanchoe species: an overview of chemical structure, biological activity and prospects for pharmacological use. Phytochem rev 16(6): 1155-1171.
CrossRef
Abbreviations
|
DCM |
Dichloro methane |
BC |
Before christ |
|
i.p. |
Intraperitoneal |
WHO |
World health organisation |
|
DPPH |
Diphenyl picryl hydrazyl |
Mm |
Millimetre |
|
NO |
Nitrogen Oxide |
Cm |
Centimetre |
|
STZ |
Streptozotocin |
mg/ml |
Milligram/Millilitre |
|
C |
Carbon |
mg/kg |
Milligram/Kilogram |
|
EE |
Ethanolic extract |
Alc. |
Alcoholic |
|
GC |
Gas chromatography |
MeOH |
Methanol |
|
MS |
Mass spectroscopy |
Aq |
Aqueous |
|
TM |
Traditional medicine |
% P |
Percentage protection |
|
CNS |
Central nervous system |
% I |
Percentage inhibition |
|
EG |
Ethylene glycol |
MOA |
Mechanism of action |
|
SGOT |
Serum glutamic acid |
SGPT |
Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase |
|
ME |
Methanolic extract |
HBA |
Hydroxy benzoic acid |
|
MIC |
Minimum inhibitory concentration |
MBC |
Minimum bactericidal concentration |
|
Bry. pin |
Bryophyllum pinnatum |
|
|

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









